Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request integration
Save yourself the work of writing custom integrations for Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request and use n8n instead. Build adaptable and scalable Development, Data & Storage, workflows that work with your technology stack. All within a building experience you will love.
How to connect Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request
Create a new workflow and add the first step
In n8n, click the "Add workflow" button in the Workflows tab to create a new workflow. Add the starting point – a trigger on when your workflow should run: an app event, a schedule, a webhook call, another workflow, an AI chat, or a manual trigger. Sometimes, the HTTP Request node might already serve as your starting point.
Popular ways to use the Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request integration
Automatic YouTube shorts generator
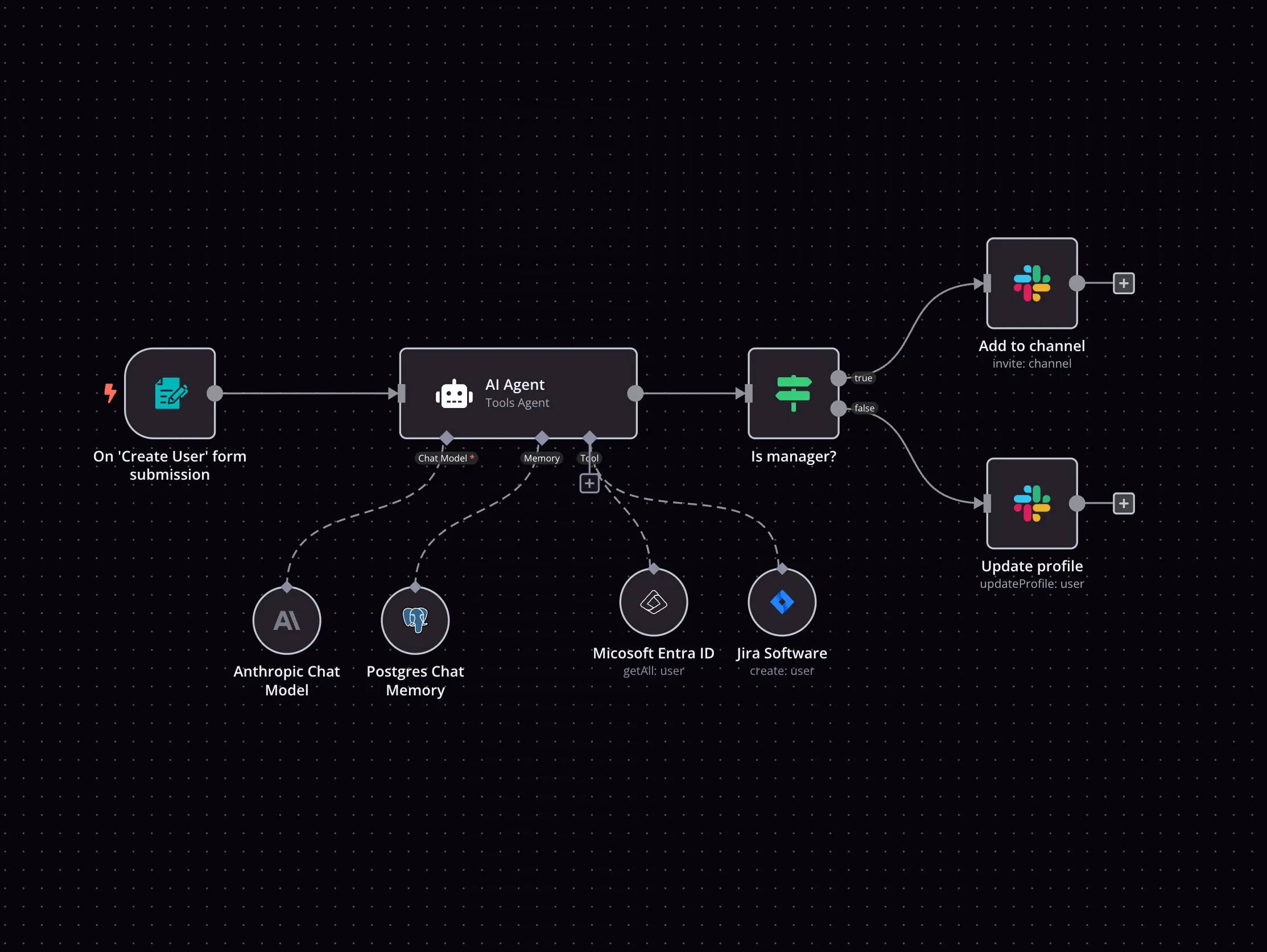
Vector database as a big data analysis tool for AI agents [1/3 anomaly][1/2 KNN]
The ultimate Instagram automation for high-quality images & text with GPT-Image
Automatically create YouTube short videos using Elevenlabs, Hailuo AI
Generate a YouTube bedtime story using OpenAI
Automate research-based newsletters with Perplexity, GPT-4, and image generation
Build your own Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request integration
Create custom Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request workflows by choosing triggers and actions. Nodes come with global operations and settings, as well as app-specific parameters that can be configured. You can also use the HTTP Request node to query data from any app or service with a REST API.
Google Cloud Storage supported actions
Create
Create a new Bucket
Delete
Delete an empty Bucket
Get
Get metadata for a specific Bucket
Get Many
Get list of Buckets
Update
Update the metadata of a bucket
Create
Create an object
Delete
Delete an object
Get
Get object data or metadata
Get Many
Retrieve a list of objects
Update
Update an object's metadata
Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request integration details
Google Cloud Storage
Data can be stored and accessed on the Google Cloud Platform infrastructure using Google Cloud Storage, a RESTful online file storage web service. The service combines cutting-edge security and sharing features with the performance and scalability of Google's cloud.
Google Cloud Storage node docs + examples
Google Cloud Storage credential docs
See Google Cloud Storage integrations
Related categories
HTTP Request
Related categories
FAQ
Can Google Cloud Storage connect with HTTP Request?
Can I use Google Cloud Storage’s API with n8n?
Can I use HTTP Request’s API with n8n?
Is n8n secure for integrating Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request?
How to get started with Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request integration in n8n.io?
Need help setting up your Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request integration?
Discover our latest community's recommendations and join the discussions about Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request integration.

Google Verification Denied
Moiz Contractor
Describe the problem/error/question Hi, I am getting a - Google hasnt verified this app error. I have Enable the API, the domain is verified on the Cloud Console, the user is added in the search console and the google do…
Open topic

HTTP request, "impersonate a user" dynamic usage error
theo
Describe the problem/error/question I a http request node, I use a Google service account API credential type. I need the “Impersonate a User” field to be dynamic, pulling data from the “email” field in the previous nod…
Open topic

Why is my code getting executed twice?
Jon
Describe the problem/error/question I have a simple workflow that retrieves an image from url with http node and prints the json/binary in code. I have a few logs, but I am confused why I see duplicate messages for each …
Open topic

How to send a single API request with one HTTP node execution, but an array of parameters in it (like emails[all]?)?
Dan Burykin
Hi! I’m still in the beginning. Now I need to make an API call via HTTP node, and send all static parameters, but with the array of emails parameter (named it wrongly just to show what I need {{ $json.email[all] }}). Wo…
Open topic

Start a Python script with external libraries - via API or Command Execution?
Tony
Hi! I have a question: I am making an app that allows a person to scrape some data via a Python library. I have a Python script that needs to be triggered after certain user actions. What is the best way to: Send a p…
Open topic
Looking to integrate Google Cloud Storage and HTTP Request in your company?
The world's most popular workflow automation platform for technical teams including
Why use n8n to integrate Google Cloud Storage with HTTP Request
Build complex workflows, really fast